
Update: This post and related images were updated on May 29, 2025 to reflect KAIST becoming an APMC node partner and on September 4, 2025 to include UTEC as an additional partner and other revisions.
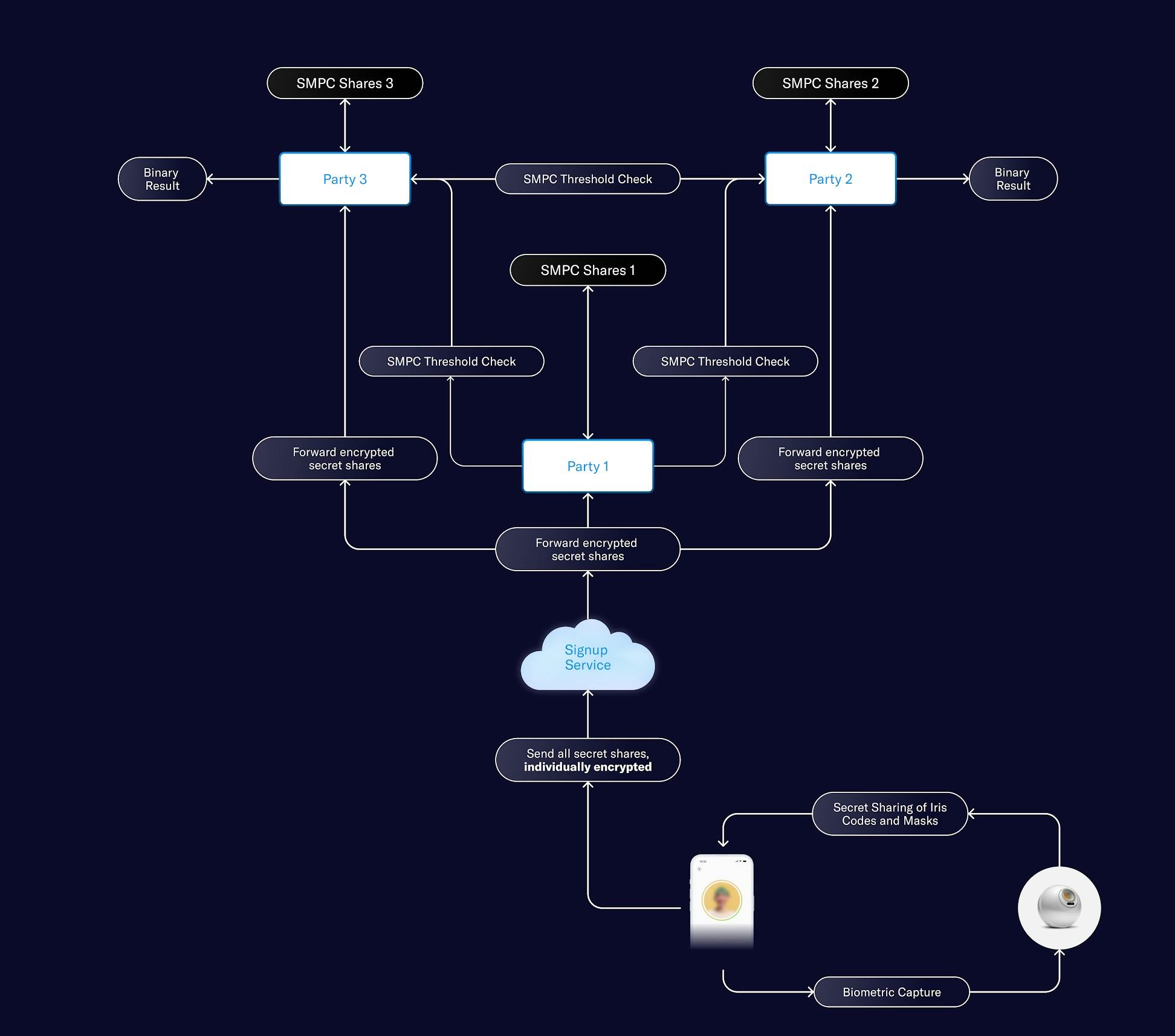
AMPC, or anonymized multi-party computation, has launched. It is the next-generation, open source quantum secure multi-party computation (MPC) setup from World that anonymizes and securely protects MPC fragments of Orb-verified World IDs. It leverages NVIDIA H100 GPUs as the main compute platform to enable up to 50 million pairwise uniqueness comparisons per second.
MPC offers additional privacy protections by eliminating the need for storing iris codes and avoiding plaintext Hamming distances during the verification process. It also operates with reputable third-parties Nethermind, the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (FAU) and UC Berkeley Center for Responsible Decentralized Intelligence (RDI), with two additional institutions - the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the University of Engineering and Technology in Peru (UTEC) - set to join the network. Today, AMPC is operated exclusively by these independent, trusted organizations, and neither World Foundation nor Tools for Humanity serve as parties in AMPC.
A new standard for privacy and performance
With the release of AMPC, The World Foundation, in collaboration with TACEO, Inversed Tech, Modulus Labs and Automata, has taken another major step forward in privacy-preserving biometric verification.
Like its predecessor (SMPC), AMPC incorporates the latest advances in cryptographic multiparty protocols and further improves on state-of-the-art techniques. This ensures that no biometric data ever leave the user's device. Instead, iris data is cryptographically processed directly on the Orb rendered anonymous and then fragmented into different encrypted shards. Only different fragments of anonymous data, which are secret shared and end-to-end encrypted, are transmitted to each compute node of the AMPC setup.
One of the key improvements in AMPC is the way similarity comparisons are handled. In the previous version, pairwise Hamming distances were used in plaintext to determine the outcome of the enrollment process. In AMPC, only a binary result is revealed: whether the user is a match or not. This approach improves privacy even further.
In addition, iris masks, which are used to filter out noise and highlight relevant features of the iris during biometric verification, are now also secret shared, ensuring that they never exist in plaintext at any stage. This eliminates another piece of information and further enhances privacy protections for users. The architecture allows users' biometrics to remain secure, private, and anonymous throughout the entire process.
Leveraging high-end hardware for superior performance
To achieve the high throughput required for global-scale biometric verification, AMPC leverages GPUs as the main compute platform. The AMPC protocol has been fully implemented using NVIDIA CUDA, enabling approximately 50 million pairwise comparisons per second overall.
Each compute node consists of an AWS p5.48xlarge instance with eight NVIDIA H100 GPUs. These instances provide around 3200 Gbps of bandwidth through Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and 20 exaflops of compute performance. This configuration is sufficient to handle the current scale of almost 7 million Orb-verified users and peak load of verifications.
Not only the uniqueness check itself, but also the transition from SMPC to AMPC was designed with the highest security and privacy in mind. This migration process, which involves changes in how the underlying cryptographic secret sharing works, is fully SMPC-based itself, meaning that no biometric data is ever processed or exposed during the upgrade. This ensures that user privacy is maintained throughout the entire transition process.
A decentralized and transparent approach
AMPC marks an important step toward decentralization and transparency.
World Foundation has partnered with Nethermind, a trusted and reputable blockchain and research engineering company, to operate an independent database in which the anonymized data is stored. Other independent operators include Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg in Germany, UC Berkeley Center for Responsible Decentralized Intelligence (RDI) in the US, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), and the University of Engineering and Technology in Peru (UTEC).

This will help create a global and decentralized system, ensuring that no entity has access to biometric data.
To further enhance community oversight, a governance board has been established, which will include independent external domain experts. This board will coordinate and supervise updates, ensure accountability, and govern the onboarding of third parties to operate compute nodes in the AMPC setup.
Scaling for the future
The future roadmap for AMPC includes numerous improvements aimed at scaling the system for future growth. These also ultimately serve to reduce the compute requirements, making it easier for new third-parties to join the network. Additionally, trusted execution environments (TEEs) are in development to minimize potential room for manipulation of those trusted AMPC parties.
Like its predecessor, AMPC is of course open source. Transparency is essential for building trust in privacy-preserving technologies, and we invite the community to review, contribute, and build upon our work.
Towards unprecedented privacy in biometric systems
AMPC is not only one of the largest SMPC based systems in production but also breaks new ground by leveraging high-end GPUs to significantly increase performance. These technologies set a new standard for privacy, security, and scalability—all while advancing the state of biometric verification.
We are proud of the advances that AMPC represents and excited about the impact it will have on protecting user privacy while enabling global-scale biometric uniqueness verification. We are also proud of the broad set of our contributors and domain experts that helped make this new upgrade possible.
For a detailed description of the techniques used in AMPC, please refer to the paper, Large-Scale MPC: Scaling Private Uniqueness Checks to Millions of Users.
Disclaimer
The above content speaks only as of the date indicated. Further, it is subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions, and so may be incorrect and may change without notice. A full disclaimer can be found in our Terms of Use and Important User Information can be found on our Risks page.
Related articles